
Virtual Local Area Networks (VLANs) play an important role in business environments by allowing organizations to better manage the ever-growing complexities of their networks. VLANs give organizations the flexibility and management capabilities that large, growing networks need.
We know that a LAN interconnects devices in a limited geographical area, i.e., in a shared physical location. Initially, devices were connected to the LAN via Ethernet cables, but now LANs use a combination of both wired and wireless connectivity. While LANs are handy, they are rigid and severely limited by their physical nature.
VLANs, on the other hand, owing to their virtual nature, can circumvent the physical limitations of LANs, allowing organizations to easily segment the networks to improve network performance, network management, and network security.
This blog post talks about Virtual Local Area Networks (VLANs), how they work, and their importance, types, and advantages of VLANs for businesses. We will cover the following topics:
- What is VLAN?
- What is the use of VLAN?
- How does VLAN work?
- What are the advantages of VLAN?
- What are the types of VLAN?
- What Is VLAN?
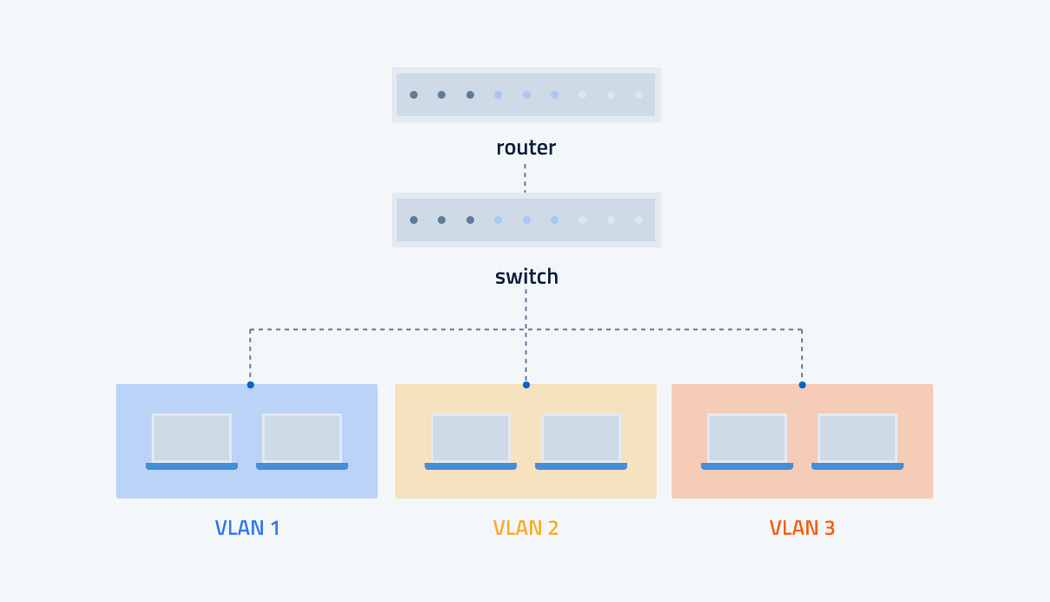
Similar to a LAN, a Virtual Local Area Network (VLAN) is a group of devices that can communicate with each other. The VLAN technology allows you to partition and isolate one or more physical LANs logically into multiple segments. Each segment or broadcast domain is regarded as a VLAN.
Although connected to a single physical network, the VLAN has the appearance and functionality of a separate network. In this context, the virtual refers to a physical object, which is recreated and altered by additional logic. Thus, VLANs allow you to keep network traffic and applications separate without having to build a separate physical network.
2. What Is The Use Of VLAN?
VLANs provide solutions for many challenges, such as network traffic congestion and data collisions, which are common in LANs. When two network nodes connected via a network hub in a LAN send data packets at the same time, data collisions occur, propagating through the entire network and increasing latency. VLANs reduce data collision incidences by sending data packets only within their broadcast domain and not to the entire network.
But VLANs are much more than mere LAN segments. Although a VLAN is physically a segment of a network, it behaves as a separate LAN. This allows you to apply separate data security rules, firewalls, and logical partitions. The logical partitions can be created based on resource needs, departments, projects, etc. Therefore, VLANs also help organizations with scalability, security, and network management.
VLANs also simplify network administration by allowing you to create partitions or groups even if network nodes are not directly connected to the same network switch. A VLAN is created by configuring network equipment through software. It does not require any relocation of devices or rewiring, greatly simplifying network design and deployment.
3. How Does VLAN Work?
VLANs are often configured to map directly to an IP (Internet Protocol) network or subnet. So, while it may appear to be operating in the network layer, it actually operates in layer 2, i.e., the data link layer of the OSI model. VLANs are generally assigned different non-overlapping network address ranges, making it possible to route data between two connected networks.
4. What Are The Advantages of VLAN?
Here is a list of advantages of using VLANs:
-
VLANs Improve Network Performance Two nodes on a network communicate by broadcasting messages to one another. The broadcast message goes out to every device on the network. Broadcasts are a necessary part of network traffic because that is how many network communications are transmitted. Network nodes get IP addresses, find network resources, and communicate with each other via broadcasts. VLANs help improve network performance by limiting broadcast traffic to within the VLAN, reducing unnecessary traffic on the entire network.
-
Enhanced Security VLANs allow you to segment your network logically, which helps you apply security policies more effectively. Sensitive data can be isolated within a VLAN, reducing the risk of unauthorized access.
-
Simplified Network Management VLANs make it easier to manage large networks by allowing administrators to group devices based on function, department, or project, regardless of their physical location. This logical grouping simplifies network management and troubleshooting.
-
Scalability VLANs provide the flexibility to add or move devices without the need for physical reconfiguration. This makes it easier to scale the network as the organization grows.
-
Reduced Cost By using VLANs, organizations can reduce the need for additional hardware, such as routers and switches, since VLANs can be configured on existing network equipment. This leads to cost savings in both hardware and maintenance.
5. What Are The Types Of VLAN?
VLANs are classified into different types based on their function or the traffic they carry. The following are the 5 main types of VLANs:
-
Default VLAN
After a switch initially boots up, all its ports become members of a default VLAN. The default VLAN makes the ports part of the same broadcast domain and allows the devices plugged into them to communicate with one another. The default VLAN generally cannot be renamed or deleted. -
Data VLAN
A data VLAN is a separate VLAN that is configured to carry only user-generated traffic. The data VLAN is also referred to as a user VLAN. -
Voice VLAN
A voice VLAN is a VLAN that is configured to carry only voice traffic. It is a common practice to have a separate VLAN for Voice over Internet Protocol (VoIP) so that it gets the necessary bandwidth, is free from congestion, and has low latency to ensure better call quality. -
Management VLAN
A management VLAN is one that is configured to access the management capabilities of a switch. This ensures that the management traffic receives the necessary bandwidth even if the user and voice traffic is high.
VLANs play a critical role in networking in a business environment. It gives network administrators granular control over their network infrastructure, facilitates scalability, improves network performance, and enhances security. It is the foundational technology for efficient network management in a dynamic business environment.





